
Home
Home
About Geosun
About Geosun
Products
Products
- Hardware
- Mobile LiDAR Scanning System
- gCollector Road Information Collection System
- gSpin POS System
- PPK Solution
Support
Support
News
News
Contact Us
Contact Us

In the realm of remote sensing and geospatial technology, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) has emerged as a cornerstone tool for capturing highly accurate 3D data of the Earth's surface. When it comes to airborne LiDAR systems, understanding the concepts of heading angle, roll angle, and pitch angle is paramount for optimizing data collection and processing. Let's delve into these fundamental aspects of airborne LiDAR and their significance.
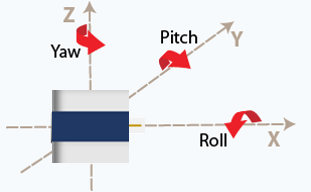
Heading Angle: Navigating the Skies
The heading angle (also named yaw angle) of an airborne LiDAR system refers to the orientation of the LiDAR sensor relative to the direction of flight. In simpler terms, it indicates which way the LiDAR sensor is pointing concerning the aircraft's forward direction. This angle is crucial for ensuring that LiDAR data is collected accurately along the desired flight path.
Imagine an aircraft equipped with a LiDAR sensor conducting a survey mission over a landscape. The heading angle determines the swath width covered by the LiDAR pulses and influences the overlap between adjacent flight lines, essential for generating a seamless and comprehensive point cloud dataset.
Roll Angle: Maintaining Stability
Roll angle pertains to the rotation of the LiDAR sensor around its longitudinal axis, which is perpendicular to the ground. In airborne LiDAR operations, maintaining a stable roll angle is essential for obtaining consistent and high-quality data.
Aircraft are susceptible to various forces and movements during flight, including banking or rolling motions. Controlling and stabilizing the roll angle of the LiDAR sensor helps minimize distortions in the collected data caused by aircraft movements, ensuring that the resulting point cloud accurately represents the Earth's surface.
Pitch Angle: Navigating Altitude
Pitch angle refers to the rotation of the LiDAR sensor around its lateral axis, which runs parallel to the aircraft's wings. This angle determines the vertical angle at which the LiDAR pulses are emitted and received concerning the horizon.
Adjusting the pitch angle is essential for controlling the altitude at which LiDAR data is collected. By modifying the pitch angle, operators can optimize the LiDAR system's performance for various survey objectives, such as terrain mapping, vegetation analysis, or infrastructure monitoring.
Optimizing LiDAR Operations
Effective airborne LiDAR data collection requires meticulous planning and execution, taking into account factors such as terrain complexity, survey objectives, and sensor specifications. Here are some key considerations for optimizing LiDAR operations:
Flight Planning: Plan flight paths and parameters carefully, considering the desired point density, terrain characteristics, and survey area coverage.
Sensor Calibration: Ensure that the LiDAR sensor is calibrated correctly before each flight to maintain data accuracy and consistency.
Motion Compensation: Implement motion compensation techniques to mitigate the effects of aircraft movements on LiDAR data quality, particularly roll and pitch variations.
Data Processing: Utilize advanced data processing algorithms and software tools to filter, classify, and analyze LiDAR point cloud data effectively.
Conclusion
Heading angle, roll angle, and pitch angle are integral components of airborne LiDAR operations, influencing the quality, accuracy, and usability of the collected data. By understanding these concepts and their implications, remote sensing professionals can optimize LiDAR survey missions to meet the diverse needs of applications such as topographic mapping, land cover analysis, urban planning, and natural resource management. As technology continues to advance, the integration of LiDAR data into geospatial workflows will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the Earth's surface and supporting informed decision-making processes.
URL:https://www.geosuntech.com/News/177.html
Previous:Understanding the Accuracy of LiDAR Point Clouds
Next:Introduction to Performance Parameters of LiDAR Scanning System




