
Home
Home
About Geosun
About Geosun
Products
Products
- Hardware
- Mobile LiDAR Scanning System
- gCollector Road Information Collection System
- gSpin POS System
- PPK Solution
Support
Support
News
News
Contact Us
Contact Us

When it comes to positioning, it's something that we are all familiar with in this era of information. Nowadays, everyone has a smartphone, and we use apps related to maps and navigation daily. These apps are based on positioning technology. Regarding positioning technology, people would think of terms like GPS and Beidou. These are all part of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). These satellites flying in space enable our smartphones to have positioning capabilities and provide us with navigation services.

The above information is well-known. Now, let me introduce a concept that may be unfamiliar to many of us. It is also related to satellites and is one of the commonly used positioning technologies in the industry, providing significant assistance to our work and daily lives. It is called RTK. So, what exactly is RTK? Why do we need it when we already have satellites? What are its characteristics, and how does it work? Don't worry, let me explain them one by one.
RTK, short for Real-Time Kinematic, is a technology that provides real-time dynamic positioning. Its full name is Real-Time Kinematic Carrier-Phase Differential Technology. Although this technology may seem professional, its underlying principles are not complicated. In short, RTK is a technique that assists GNSS.
Why do we need to assist GNSS? It's because GNSS has its limitations! Satellite positioning is subject to errors. These errors arise from both internal and external factors. For example, errors occur when satellite signals pass through the ionosphere and troposphere. Other sources of errors include Doppler effects caused by high-speed satellite movement, multipath effects, channel errors, satellite clock errors, ephemeris errors, internal noise errors, and so on. Some of these errors can be eliminated, while others can only be partially eliminated or cannot be eliminated at all. They affect the accuracy and reliability of the GNSS system. To better eliminate errors and improve positioning accuracy, experts have developed a more advanced positioning technology known as RTK.
Let's look at the working principle of RTK.
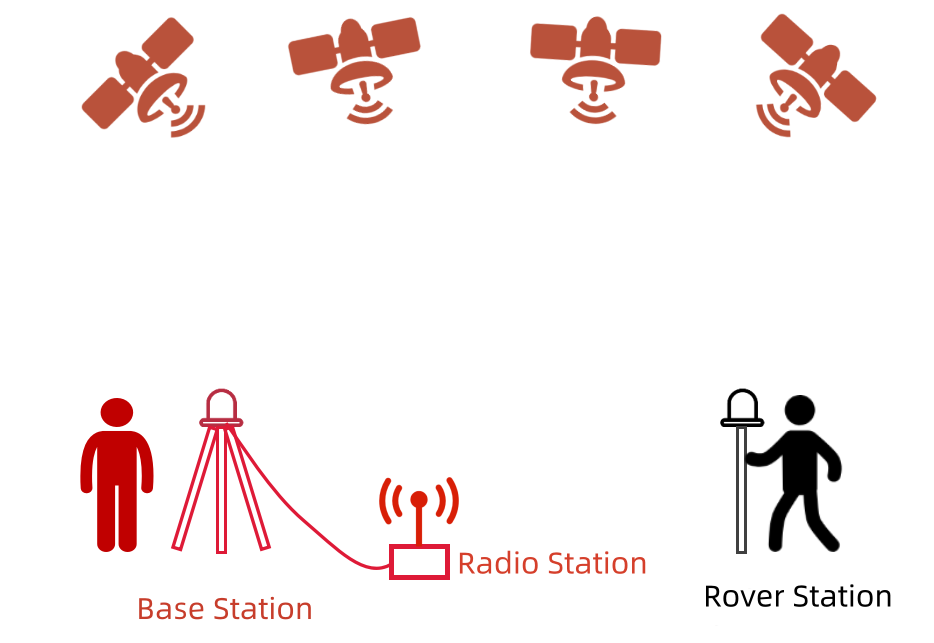
As shown in the above diagram, this is a standard configuration of a traditional RTK network. In addition to satellites, the RTK system consists of two essential components: the base station and the rover station.
Both stations are equipped with satellite receivers to observe and receive satellite data. As the name suggests, the base station serves as the reference station, providing a known reference position. The rover station, on the other hand, is a mobile station that continuously moves. The rover station is the object target that measures its three-dimensional coordinates, which is typically the user end. You often see people outdoors carrying tripods for measurements. Some of them might be carrying RTK base stations or rover stations.
Now let's examine the positioning process.
First, the base station, serving as the measurement reference, is usually placed in an open area with good visibility. The three-dimensional coordinate information of the base station is generally known.
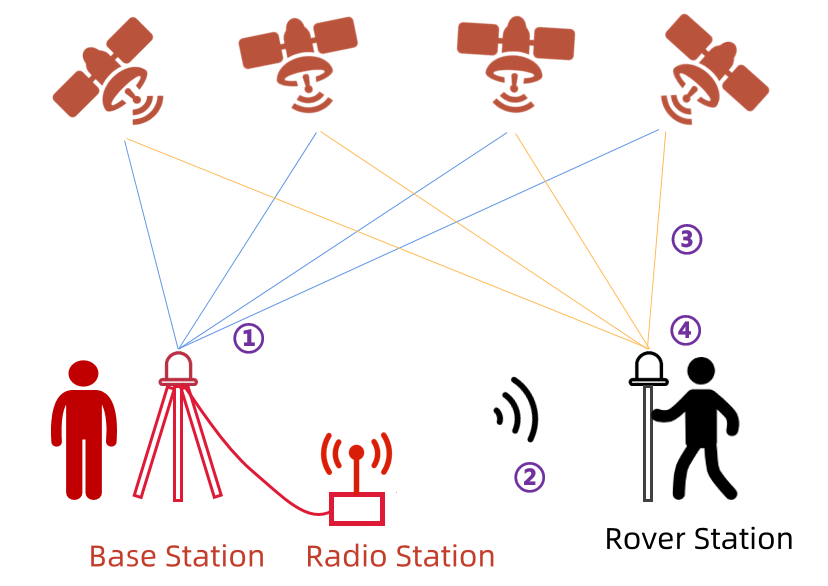
Step 1: The base station starts by observing and receiving satellite data.
Step 2: The base station transmits the observed data in real time to the rover station through a nearby radio station (data link), typically within a distance of no more than 20km.
Step 3: While receiving data from the base station, the rover station also observes and receives satellite data.
Step 4: Based on the data received from the base station and its data, the rover station performs real-time differential calculations using relative positioning principles. This process allows the rover station to compute its three-dimensional coordinates and accuracy, with positioning accuracy reaching 1cm to 2cm. With that, the measurement is completed.
As you can see, RTK technology offers several advantages, such as no requirement for line-of-sight communication between observing stations, high positioning accuracy, simple operation, and all-weather operation. It is an excellent positioning technology.
Earlier, we discussed traditional RTK technology, which is a basic model of RTK. Traditional RTK implementation is simple and cost-effective. However, it has a significant limitation: the distance restriction between the rover station and the base station.
The farther the distance, the greater the difference in error factors, leading to decreased positioning accuracy. Moreover, if the distance exceeds the communication range of the radio station, it becomes impossible to work.
To overcome the limitations of traditional RTK technology, network RTK technology was introduced in the mid-1990s. In network RTK technology, multiple base stations (three or more) are uniformly distributed in a larger area, forming a network of base stations.
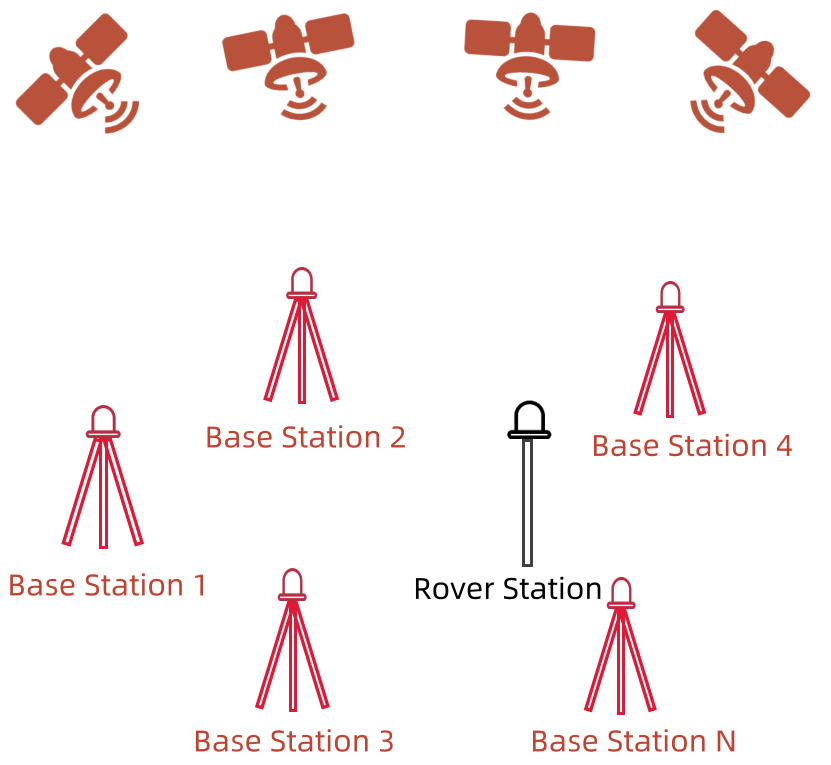
In this case, does the rover station need to be compared and calculated with each base station individually? No, that would be too cumbersome.
In network RTK, a regional GNSS network error model is used instead of a single-point GNSS error model. The base station network sends data to a central server, which then simulates a "virtual base station" based on the data. (Hence, network RTK is also known as "virtual base station technology" or "virtual reference station technology".) The rover station only "sees" this "virtual base station." Based on the data sent by this "virtual base station," the rover station completes the final measurement calculations.
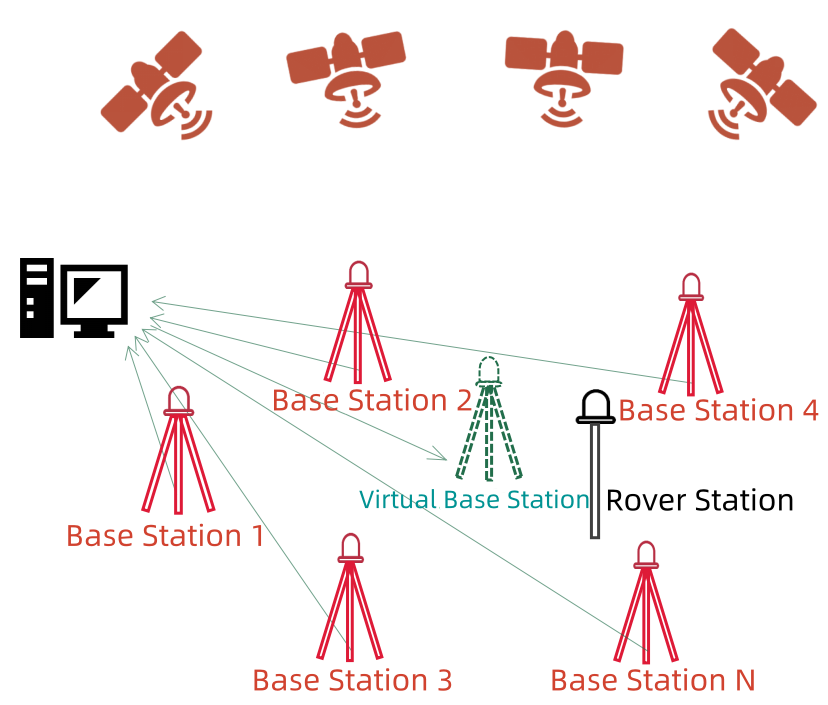
The advantages of network RTK are evident. As you may have noticed, the mobile communication base stations we usually see can also serve as "base stations." Base stations are everywhere around us, which means network RTK achieves seamless coverage.
The communication between the rover station and the central server can be accomplished through the built-in wireless communication module in the rover station (terminal). These high-precision positioning modules integrate RTK technology and serve as mobile communication modules, enabling the aforementioned functionalities.
Furthermore, for users, there is no need to establish their base stations, which saves a significant amount of cost (only requiring some communication fees).
Lastly, network RTK offers higher accuracy and reliability. With multiple base stations, even if one or two of them malfunction, it has a minimal impact.
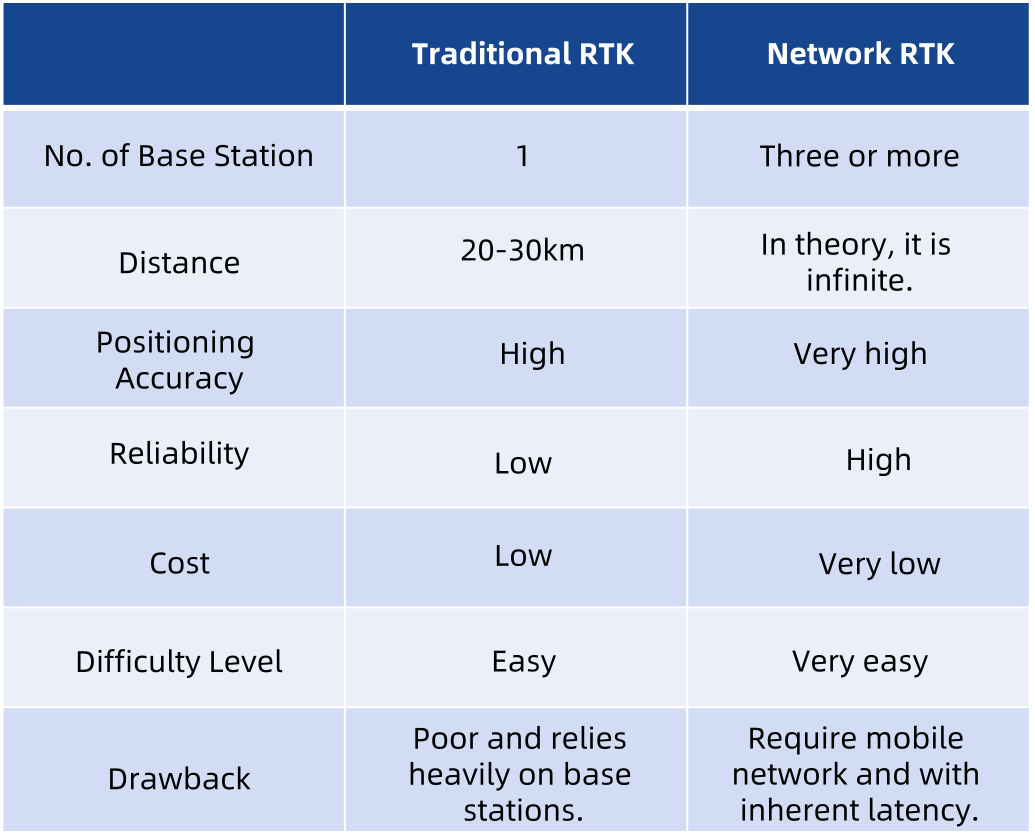
It is worth mentioning that in the network RTK model, the stability of the network has a significant impact on positioning accuracy. It is essential to ensure stable network communication to guarantee the stable transmission of differential data, thereby achieving ultra-high positioning accuracy.
After years of accumulation, RTK technology has become increasingly mature. Its characteristics of high accuracy, high speed, and high stability have made it widely used in fields such as surveying and mapping, unmanned aerial vehicles, vehicle navigation, and security. Geosun Navigation GS-100G handheld LiDAR scanner combines SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), a real-time localization and mapping technology, with RTK (Real-Time Kinematic), a centimeter-level satellite differential positioning technology, to achieve scanning and mapping in unknown environments such as indoor and outdoor spaces without relying on GPS or other GNSS positioning. It can also be used in open outdoor environments with the assistance of differential positioning systems to directly correct cumulative errors, enabling the entire system to obtain higher-precision point cloud data in a wide range of outdoor acquisition processes without the need for loop closure.
In the future, RTK technology will continue to evolve towards longer distances, higher precision, multi-frequency and multi-mode capabilities, and greater stability. Let us wait and see!
URL:https://www.geosuntech.com/News/223.html
Previous:How Much do You Know About LiDAR in Surveying Applications?




