
Home
Home
About Geosun
About Geosun
Products
Products
- Hardware
- Mobile LiDAR Scanning System
- gCollector Road Information Collection System
- gSpin POS System
- PPK Solution
Support
Support
News
News
Contact Us
Contact Us

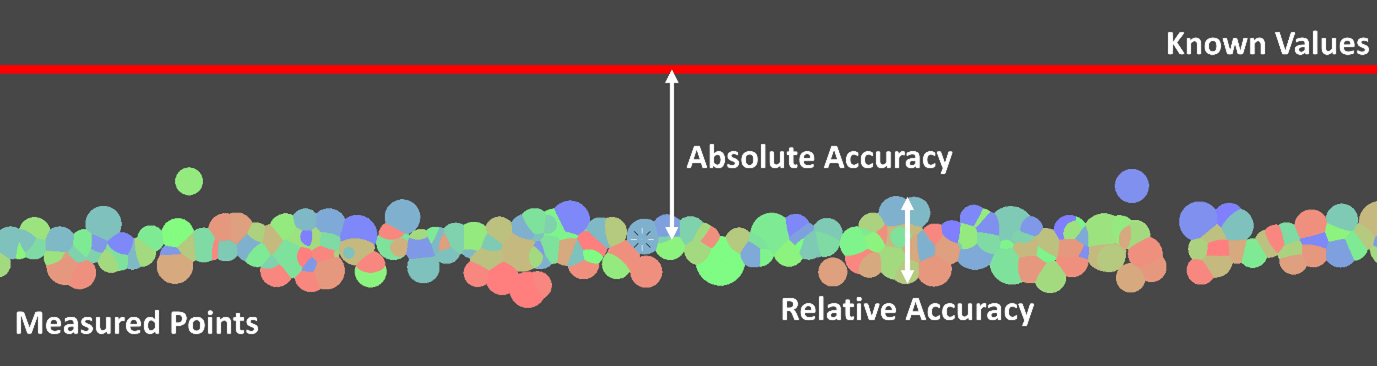
When working with LiDAR technology, understanding the distinctions between relative accuracy and absolute accuracy is crucial. Whether you're mapping landscapes, creating 3D models, or conducting surveys, these concepts significantly impact your results. Let's dive into what these terms mean and how they affect LiDAR applications.
LiDAR is a remote sensing method that uses laser light to measure distances between the sensor and the Earth's surface. This technology generates precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics. LiDAR data is commonly used in forestry, environmental monitoring, urban planning, and topographic mapping.
Relative accuracy refers to the precision of measurements concerning one another within a dataset. In simpler terms, it answers the question: "How accurate are the measurements relative to each other?"
Contextual Measurement: Relative accuracy is concerned with how well points or features in the LiDAR data relate to each other. For example, if you measure the height of two trees, relative accuracy assesses how accurately their heights are represented in relation to one another.
Influenced by Environmental Factors: Factors like sensor calibration, atmospheric conditions, and point density can influence relative accuracy. If the LiDAR system is well-calibrated, measurements will reflect true differences even if the absolute values are off.
Use Cases: Relative accuracy is particularly important in applications where the spatial relationship between features matters, such as in flood modeling, where understanding the height difference between land and water is critical.
Absolute accuracy, on the other hand, refers to the accuracy of measurements in relation to a defined coordinate system or a known point on the Earth's surface. It answers the question: "How close are my measurements to the true values?"
Fixed Reference: Absolute accuracy uses a fixed reference point, like GPS coordinates, to determine how close LiDAR measurements are to their true geographic locations.
Crucial for Navigation and Mapping: In applications where exact positioning is critical—such as in civil engineering or boundary mapping—absolute accuracy ensures that the data corresponds accurately to real-world locations.
Validation Required: Achieving high absolute accuracy often requires validation against ground control points (GCPs) or established reference datasets.
| Feature | Relative Accuracy | Absolute Accuracy |
| Definition | Accuracy of measurements relative to each other | Accuracy of measurements against a fixed reference |
| Measurement Focus | Internal consistency within the dataset | External validation against real-world coordinates |
| Importance | Critical for assessing spatial relationships | Essential for precise location-based applications |
| Calibration | Relies on internal calibration processes | Requires external validation and ground truthing |
| Common Uses | Environmental monitoring, feature analysis | Mapping, navigation, construction surveying |
In many LiDAR applications, both relative and absolute accuracy are essential. For instance, when mapping a forest, you might need to ensure that the relative heights of trees are accurately represented (relative accuracy) while also ensuring that the entire dataset is correctly positioned in relation to a geographical coordinate system (absolute accuracy).
Understanding the differences between relative and absolute accuracy in LiDAR scanning is crucial for professionals in various fields. While relative accuracy provides insights into the relationships between data points, absolute accuracy ensures those points are accurately placed within the real world. By focusing on both types of accuracy, you can enhance the quality and reliability of your LiDAR data, leading to more effective analyses and better decision-making.
Improving relative accuracy often involves ensuring proper sensor calibration and optimizing point density during data collection.
To enhance absolute accuracy, ground control points (GCPs) are often used for validation and correction of the LiDAR data against known geographic coordinates.
While it is possible to use LiDAR data without GCPs, the absolute accuracy may be compromised. For applications requiring high precision, using GCPs is recommended.
By understanding and applying both relative and absolute accuracy principles, you can significantly improve the outcomes of your LiDAR scanning projects.
URL:https://www.geosuntech.com/News/254.html
Previous:Hyperspectral Imaging vs. Multispectral Imaging: Which is Right for You?
Next:SLAM vs. GNSS for LiDAR Surveying: A Comprehensive Comparison




