
Home
Home
About Geosun
About Geosun
Products
Products
- Hardware
- Mobile LiDAR Scanning System
- gCollector Road Information Collection System
- gSpin POS System
- PPK Solution
Support
Support
News
News
Contact Us
Contact Us

In the field of LiDAR technology, understanding the distinction between accuracy and precision is fundamental. These terms are often mentioned together but refer to different qualities of LiDAR data, both essential for professionals in 3D mapping, surveying, and spatial analysis. Whether you’re focused on LiDAR data quality, point cloud accuracy, or measurement precision, knowing the difference between accuracy and precision will help you select the right LiDAR scanner and achieve the best results.
This article explores what accuracy and precision mean in the context of LiDAR technology and why both are critical for reliable data collection.
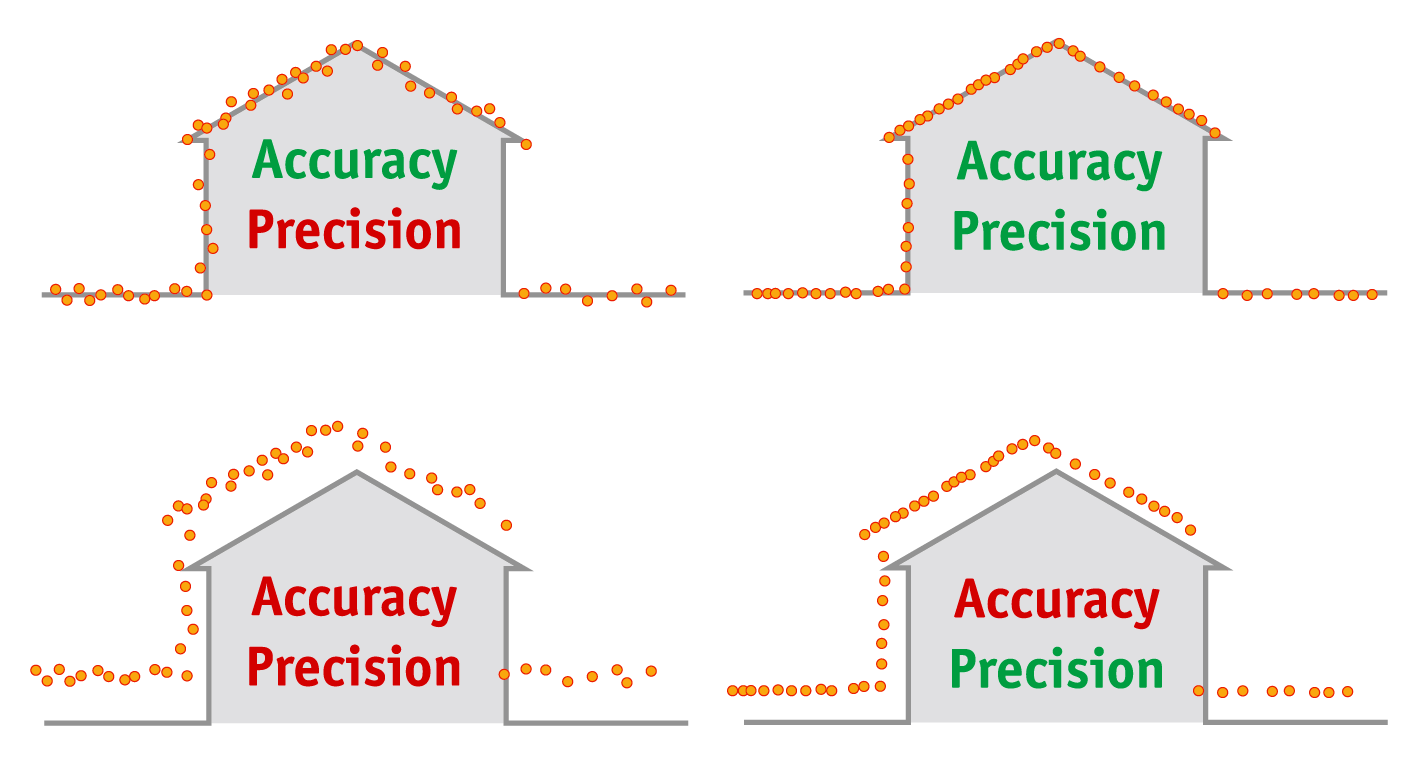
Accuracy in LiDAR refers to how closely the measurements align with the real-world values of the scanned environment. For instance, if a LiDAR scanner measures the distance to an object 100 meters away, a highly accurate scanner would record this measurement as close to 100 meters as possible. This ensures that each LiDAR point in the 3D point cloud matches the real-world position.
Factors that influence LiDAR accuracy include:
Hardware quality: High-quality lasers, sensors, and GPS modules improve overall accuracy.
Calibration: Proper calibration aligns all components, minimizing error.
Environmental conditions: Weather, lighting, and even terrain can impact accuracy.
In applications like topographic surveying, construction mapping, or 3D geospatial modeling, accuracy is essential, as precise measurements can reduce the need for manual corrections and provide confidence in spatial data accuracy.
Precision refers to the consistency of LiDAR measurements. A precise LiDAR system provides repeatable, consistent results under the same conditions, even if these results are not perfectly accurate. Precision is more about the “tightness” or clustering of data points rather than their exact real-world alignment.
Consider a LiDAR system that measures the same object multiple times: a highly precise system will yield measurements that are very close to each other, indicating reliable repeatability.
Applications that benefit from high precision include:
3D modeling: Where high-density, consistent point clouds are required.
Structural analysis and monitoring: To detect small-scale changes in buildings or infrastructure.
Environmental monitoring: For repeated scans to observe gradual changes over time.
With precision, you're focusing on the system’s ability to replicate measurements. This quality is particularly valuable in applications like forestry mapping, site monitoring, or any field where tracking change is important.
For reliable LiDAR data, both accuracy and precision are important, but they serve different purposes:
Accuracy ensures the data points align closely with the actual world, ideal for tasks requiring absolute positioning.
Precision ensures repeatable, consistent measurements, useful for applications that detect subtle changes over time.
Imagine using a LiDAR scanner for urban planning. High accuracy is needed to ensure each feature aligns with its actual position, essential for infrastructure planning. Precision, however, allows the scanner to produce detailed, consistent scans so designers and engineers can rely on repeat measurements.
Most LiDAR survey systems aim to balance accuracy and precision, though some may emphasize one over the other depending on the application’s requirements.
When selecting a LiDAR system, consider your application’s specific needs:
If accuracy is paramount—for land surveying, infrastructure development, or boundary mapping—choose a LiDAR system with high accuracy specifications and advanced calibration. High accuracy ensures that measurements closely match real-world coordinates.
If precision is critical—for applications like 3D modeling, structural monitoring, or forestry—look for systems with high repeatability to produce consistent data sets, even if absolute accuracy is slightly lower.
For balanced needs—such as aerial LiDAR mapping, UAV-based mapping, or city modeling—opt for a system that combines strong accuracy and precision to capture detailed, reliable data for large and complex environments.
In summary, while accuracy and precision are often mentioned together, they play different roles in LiDAR mapping and 3D scanning. Accuracy focuses on alignment with real-world coordinates, while precision focuses on repeatability. Both are essential for producing reliable LiDAR data, but the priority will depend on your specific LiDAR application.
Understanding these differences can guide you to the right LiDAR equipment for your projects, ensuring you obtain high-quality, actionable data that meets both accuracy and precision requirements. Whether you’re focused on capturing large terrains or tracking small changes, achieving the right balance between accuracy and precision will elevate your LiDAR survey results.
URL:https://www.geosuntech.com/News/256.html
Previous:SLAM vs. GNSS for LiDAR Surveying: A Comprehensive Comparison
Next:DEM, DTM, and DSM: Understanding Key Elevation Models in GIS




