
Home
Home
About Geosun
About Geosun
Products
Products
- Hardware
- Mobile LiDAR Scanning System
- gCollector Road Information Collection System
- gSpin POS System
- PPK Solution
Support
Support
News
News
Contact Us
Contact Us

In today's rapidly advancing technology landscape, a technology called semi-solid-state LiDAR has quietly emerged, attracting countless attentions with its unique advantages and extensive application prospects. So, what exactly is semi-solid-state LiDAR? And what are its uses? Let's explore the mysteries of this technology and its practical applications together.
Semi-solid-state LiDAR is a new type of laser detection technology that falls between traditional solid-state LiDAR and non-solid-state LiDAR. Compared to traditional mechanical LiDAR systems, semi-solid-state LiDAR achieves higher reliability and lower costs by reducing the number of moving mechanical parts. At the same time, it retains the core functionality of LiDAR, which is to measure the distance, velocity, and other properties of target objects by emitting laser pulses and receiving the reflected light signals.
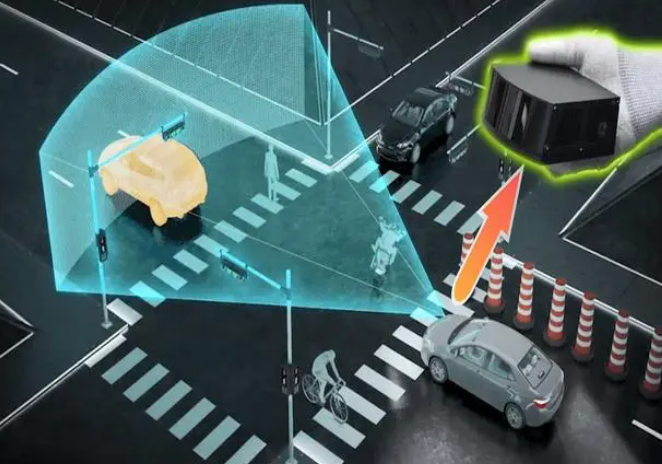

The working principle of semi-solid-state LiDAR can be likened to a bee gathering nectar from a flower. Just as a bee can accurately locate flowers and extract nectar from them, semi-solid-state LiDAR can precisely emit laser beams and receive signals reflected from various objects. These signals, after processing, can generate detailed three-dimensional images of the surrounding environment, providing crucial navigation information for applications like autonomous vehicles, drones, and more.
In the field of autonomous driving, the application of semi-solid-state LiDAR is particularly prominent. Imagine a scenario where an autonomous vehicle is navigating through busy streets, needing precise awareness of pedestrians, vehicles, and obstacles around it. At this moment, a car equipped with semi-solid-state LiDAR is akin to having a pair of super eyes, capable of "seeing" road conditions even in adverse weather conditions such as rain and fog, ensuring safe driving.
Apart from autonomous driving, semi-solid-state LiDAR also plays an important role in many other fields. For example, in archaeology, it can be used to scan ancient sites, helping us understand the structure of ancient buildings. In forestry management, it can assist in monitoring the growth status of forests and the occurrence of pests and diseases. In agriculture, it can be used for precision agriculture, guiding farmers in crop planting and management.
Certainly, the applications of semi-solid-state LiDAR extend far beyond those mentioned. In disaster relief efforts, it can rapidly generate topographic maps of disaster areas, aiding rescue teams in efficient search and rescue operations. In environmental monitoring, it can provide real-time monitoring of air quality and the distribution of pollutants, safeguarding our health and well-being.
What's the Difference Between Semi-solid-state and Solid-state LiDAR?
The main differences between semi-solid-state LiDAR and solid-state LiDAR lie in their scanning methods, internal structures, and field of view. The specific differences are analyzed as follows:
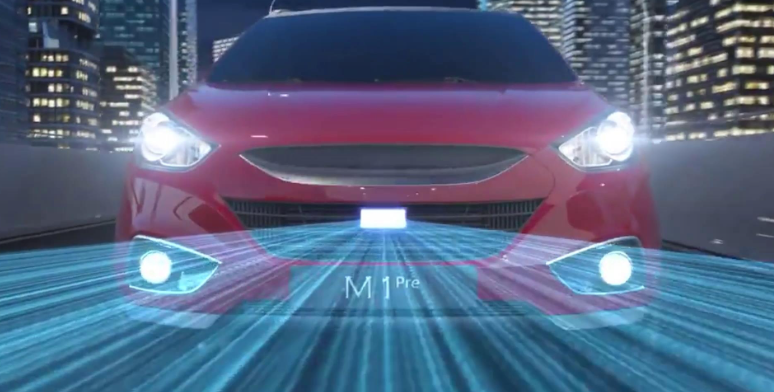
Scanning Method: In semi-solid-state LiDAR, both one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) scanning methods are utilized. One-dimensional scanning involves scanning along a single axis, typically either horizontally or vertically, while two-dimensional scanning involves scanning along both horizontal and vertical axes simultaneously. Solid-state LiDAR, on the other hand, primarily consists of two main technological approaches: Optical Phased Array (OPA) and Flash LiDAR.
Internal Structure: In semi-solid-state LiDAR, various components such as rotating mirrors, Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS), or prisms may be employed to achieve partial directional scanning. These components are responsible for directing the laser beams emitted by the lidar system across the field of view. While these mechanisms enable scanning along certain directions, they typically involve moving parts and mechanical motion. In contrast, full solid-state LiDAR systems do not contain any moving parts internally. Instead, they utilize semiconductor technologies to emit, scan, and receive laser beams.
Field of View: Mechanical LiDAR systems typically achieve a 360° field of view by utilizing rotating mirrors or other mechanical scanning components to direct laser beams in all directions around the sensor. This allows for comprehensive coverage of the surroundings without blind spots. Semi-solid-state LiDAR systems, on the other hand, typically have a narrower field of view, usually around 120°. This limited field of view is due to the constraints of the scanning mechanisms used, such as MEMS mirrors or prisms, which may not be able to cover the full 360° without additional complexity.
Generally speaking, there are differences in scanning methods between semi-solid-state and solid-state LiDARs. While semi-solid-state LiDARs aim to reduce costs and improve reliability by minimizing moving parts while maintaining certain performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, semi-solid-state LiDAR is a fascinating technology that not only possesses the high precision of traditional LiDAR but also offers improved stability and cost-effectiveness. With ongoing technological advancements and expanding applications, semi-solid-state LiDAR will play an increasingly significant role on the future stage of technology, bringing more convenience and safety to our lives.
URL:https://www.geosuntech.com/News/198.html
Previous:How Solid-State LiDAR Technology is Revolutionizing Cost Efficiency




