
Home
Home
About Geosun
About Geosun
Products
Products
- Hardware
- Mobile LiDAR Scanning System
- gCollector Road Information Collection System
- gSpin POS System
- PPK Solution
Support
Support
News
News
Contact Us
Contact Us

In the realm of remote sensing and 3D mapping, two terms often surface: LiDAR and laser scanners. While they may seem synonymous, there are critical distinctions between the two technologies. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the dissimilarities, applications, and advantages of LiDAR and laser scanners.

Fundamental Technology
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR operates by emitting rapid pulses of laser light and measuring the time it takes for these pulses to return after hitting objects in the environment. By calculating the time delay and knowing the speed of light, LiDAR systems can precisely determine the distance to various surfaces, thus creating detailed 3D maps of the surroundings.
Laser Scanners: Laser scanners, on the other hand, utilize lasers to scan and measure distances to objects in their field of view. Unlike LiDAR, which often involves a single laser beam, laser scanners can employ multiple laser beams to capture detailed information about the objects being scanned.

Applications
LiDAR: LiDAR finds extensive use in applications such as topographic mapping, forestry, urban planning, archaeology, autonomous vehicles, and infrastructure monitoring. Its ability to generate highly accurate elevation models and detailed point clouds makes it indispensable in various industries.
Laser Scanners: Laser scanners are commonly employed in industrial metrology, quality control, reverse engineering, and construction. They excel at capturing precise geometric measurements of objects, facilitating tasks like 3D modeling, inspection, and analysis in manufacturing and engineering processes.
Range and Resolution
LiDAR: LiDAR systems typically offer long-range capabilities, allowing them to collect data over vast areas from considerable distances. Moreover, they can achieve high spatial resolution, capturing intricate details of the terrain or objects being scanned. Laser Scanners: Laser scanners often excel in capturing fine details with high accuracy but may have limited range compared to LiDAR systems. However, advancements in technology have enabled some laser scanners to achieve impressive scanning ranges while maintaining excellent resolution.
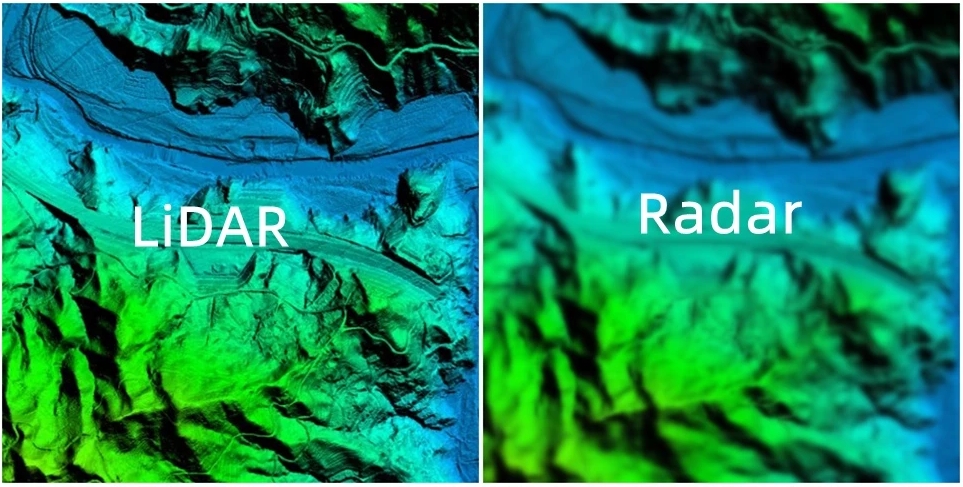
Mobility and Versatility
LiDAR: LiDAR systems are commonly mounted on airborne platforms such as airplanes and drones, as well as ground-based vehicles. This mobility enables them to cover large areas efficiently and capture data from various perspectives.
Laser Scanners: Laser scanners come in various forms, including handheld, tripod-mounted, and robotic systems. This versatility allows them to be deployed in diverse environments, ranging from manufacturing facilities and construction sites to archaeological digs and crime scenes.
Cost Considerations
LiDAR: While LiDAR technology offers unparalleled accuracy and data quality, it often comes with a higher price tag due to the complexity of the systems and the advanced sensors involved. However, the cost of LiDAR solutions has been steadily decreasing as the technology becomes more widespread and accessible.
Laser Scanners: Laser scanners, particularly handheld and tripod-mounted models, tend to be more affordable compared to LiDAR systems. This makes them a viable option for smaller-scale projects or applications where extreme precision may not be necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both LiDAR and laser scanners utilize laser technology for capturing spatial data, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different applications. LiDAR excels in large-scale mapping and environmental monitoring, whereas laser scanners shine in precise measurement and industrial applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most suitable technology for specific project requirements and maximizing the efficiency and accuracy of data collection processes.
URL:https://www.geosuntech.com/News/185.html
Previous:MEMS LiDAR: A Emerging Technology for Autonomous Driving
Next:Inertial Navigation vs Integrated Navigation, What is the Difference?




